Stroke is the third leading cause of death in Malaysia. Worldwide, it is the second commonest cause of death and a leading cause of adult disability. Every year, millions of people suffer a stroke. It is also among the top four leading causes of death in ASEAN countries, with the crude death rate ranging from 10.9/100 000 (Thailand) to 54.2 per 100 000 (Singapore).
Source: www.bcenter.com
What is stroke?
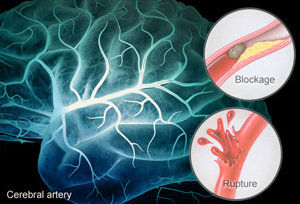
Stroke is a condition when the brain loses it is blood supply either due to blood vessel blockages (thrombosis), blood vessel narrowing (stenosis) or rupture of the brain blood vessels causing bleeding in the brain. There are two forms of stroke:- ischemic or hemorrhagic.
How do strokes happen?
In ischemic stroke – blood vessels in the brain gets blocked by formation of clot inside the vessel (a thrombus), a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque or by an emboli (a clot that travelled in the bloodstream which subsequently gets lodged in the brain blood vessels).
In hemorrhagic stroke, it occurs when there is an aneurysm or blood vessel malformation in the brain ruptures and bleeds into the brain. It is commonly associated with uncontrolled hypertension.
Do you know that 80% of stroke events can be prevented?
Stroke can be prevented if everyone takes step to avoid it from occurring. Never think that you have no risk to get stroke. Anyone can get a stroke – regardless whether you are a man or a woman, young or old, all ethnicities.
What you can do to avoid stroke.
- Control your blood pressure if you are hypertensive. Monitor daily and remember to take your blood pressure medication daily. Do not self adjust or stop your medication without advise from your doctor
- Stop smoking! A smoker has double the risk to get stroke compared to a non smoker.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Healthy and balanced diet
- Diabetics should aim for optimum sugar control.
- Get checked for heart rhythm abnormality
- Exercise and stay active
- Avoid or cut down your alcohol intake
How do you know if you are having a stroke?
You might be having a stroke if you have :-
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg especially if limited to just one side of the body
- Sudden difficulty in swallowing
- Abrupt change in consciousness, more drowsy, having trouble speaking or understanding
- Inability to see in one or both eyes
- Unstable when walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause which is accompanied with vomiting and nausea

Source: www.bcenter.com
If you witness someone having any of the above symptoms, you can use FAST to quickly assess whether or not that person has a stroke
- F for FACE: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
- A for ARMS: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- S for SPEECH: Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. Is their speech slurred or strange?
- T for TIME: If you observe any of these signs, seek medical attention immediately.
What do you do if you or a loved one has early signs of stroke?
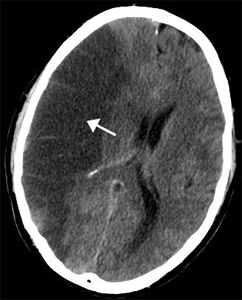
Get them as fast as possible to the hospital for assessment. Every minute counts when someone is having a stroke. The longer blood stopped flowing into the brain, the greater the damage and recovery would be poorer. Once in the hospital, doctors there will use a brain imaging scan technique, either a Computed Tomography (CT) or a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan to decide what type of stroke the patient might have.
Source: www.wikipedia.com
If they are having ischemic stroke, they can be treated with a drug called rt-PA. This drug dissolves blood clots that obstruct the blood flow to the brain. Unfortunately, this drug cannot be given for all stroke cases. The treatment works best if given within four and half hours from the stroke event onset. In order for a patient to get assessed and receive this treatment, the patient needs to get to the hospital with stroke thrombolysis facility within 60 minutes.
A five-year study by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) found that stroke patients who received rt-PA within three hours of the start of stroke symptoms were at least 30 percent likelier to recover with little or no disability after three months.
If they are having hemorrhagic stroke, doctors can control bleeding by controlling blood pressure. In the event of massive intracranial bleed which does not respond to pharmacological (drug) treatment, we may even need to get neurosurgeons to intervene by doing an operation to relieve the pressure effects in the brain caused by the bleeding.
What to expect if you or your loved one suffer from a stroke?
Even with the best medical care, as many as two-thirds of patients suffering from stroke will die due to stroke or its complications; or end up with permanent disability. Having a stroke can be a life devastating event for victims and their loved ones. Stroke patients and their families need our full support in order to recover from this event.
Recovery from stroke is a lifelong process. Do not be discouraged if they take a long time to recover from a stroke event. Different patients recover at different rates. The sooner rehabilitation starts – the better the outcome. If your loved one had a stroke, there are many things you can do as a caregiver.
- Identify risk then control or eliminate them – if not, stroke may strike again. The most important thing you can do after a stroke is to avoid another stroke, which can cause further damage to the brain and cause worsening disability.
- Get them to move – many stroke patients do not die from stroke itself – they die from complication of being unable to move. Moving patients limb at regular intervals can prevent complications such as pressure sores, aspiration pneumonias, pulmonary embolism etc. Sit the patient up and help them undergo regular physiotherapy so that they can move better.
- Remember to take medications – stroke patients will need to be on life-long blood thinning agents and cholesterol lowering medications. These medications help to prevent recurrent episodes of stroke. They also need to monitor their blood pressure and sugar regularly.
- Prevent falls by taking necessary precautions – A stroke patient can fall easily. They may hurt themselves in the process. You may need to make adjustments in the home environment to prevent falls from happening. If your loved one frequently falls more than twice a month, seek your physician’s advice on how to prevent further falls.
- Watch out for depression – Many stroke patients have difficulty to adjust to life post stroke. For someone who is active and independent, having to be bed-bound and dependent on others after a stroke can be very frustrating. Depression in stroke patients may hinder recovery as patients lose their motivation to recover. Get help if you notice any changes in their mood or behaviour.
- Seek support in other people and take care of yourself – Carer stress can break a caregiver. Get other family members as well as community to help you. Take turns to take a break from caregiving with other carers. As a caregiver, you also have the right to get adequate rest. Aim to eat a balanced meal, exercise or you can go out socializing to keep you continue feel positive.
Further information on community support for stroke patients and carers
NASAM – National Stroke Association of Malaysia http://www.nasam.org
Dr. Nur Hidayati is an internal medicine specialist with special interest in infectious disease and nephrology. She is a permanent columnist for the Malaysian Medical Gazette. Learn more about her on The Team page.
References
- Malaysian CPG Management of ischemic stroke 2012
- “Know Stroke. Know the Signs. Act in Time.”, NINDS. January 2008
- Evidence Based Stroke Rehabilitation Review http://www.ebrsr.com/uploads/Executive-summary-SREBR-15.pdf
[This article belongs to The Malaysian Medical Gazette. Any republication (online or offline) without written permission from The Malaysian Medical Gazette is prohibited.]
